SEO Title: What Does AVM Stand For In Real Estate? A Complete Guide
Meta Description: An AVM, or Automated Valuation Model, is a software algorithm that instantly estimates a property's market value using big data. Learn how AVMs work.
Meta Keywords: what does avm stand for in real estate, automated valuation model, real estate avm, avm accuracy, what is an avm, property valuation
An AVM in real estate stands for Automated Valuation Model, a software program using statistical modeling and massive datasets to generate a property’s market value instantly. Over 90% of online home value estimators use AVM technology, but its primary function is powering institutional-grade portfolio analysis and loan underwriting for lenders and investors.
This guide breaks down exactly how AVMs work, their accuracy benchmarks, and their limitations. An AVM is a high-speed, data-driven appraisal that occurs entirely behind a screen, providing a crucial starting point for any real estate analysis.
| Core Takeaway | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | An algorithm that calculates property value using public records, MLS data, and market trends. |
| Primary Use | Fast, low-cost property valuation for portfolio analysis, loan pre-qualification, and investment screening. |
| Key Metrics | Professional AVMs provide a Confidence Score and Forecast Standard Deviation (FSD) to measure reliability. |
| Limitations | AVMs cannot physically inspect a property and struggle with unique homes or areas with sparse sales data. |
This article will now detail the mechanics, applications, and accuracy of Automated Valuation Models.
What Is an Automated Valuation Model?
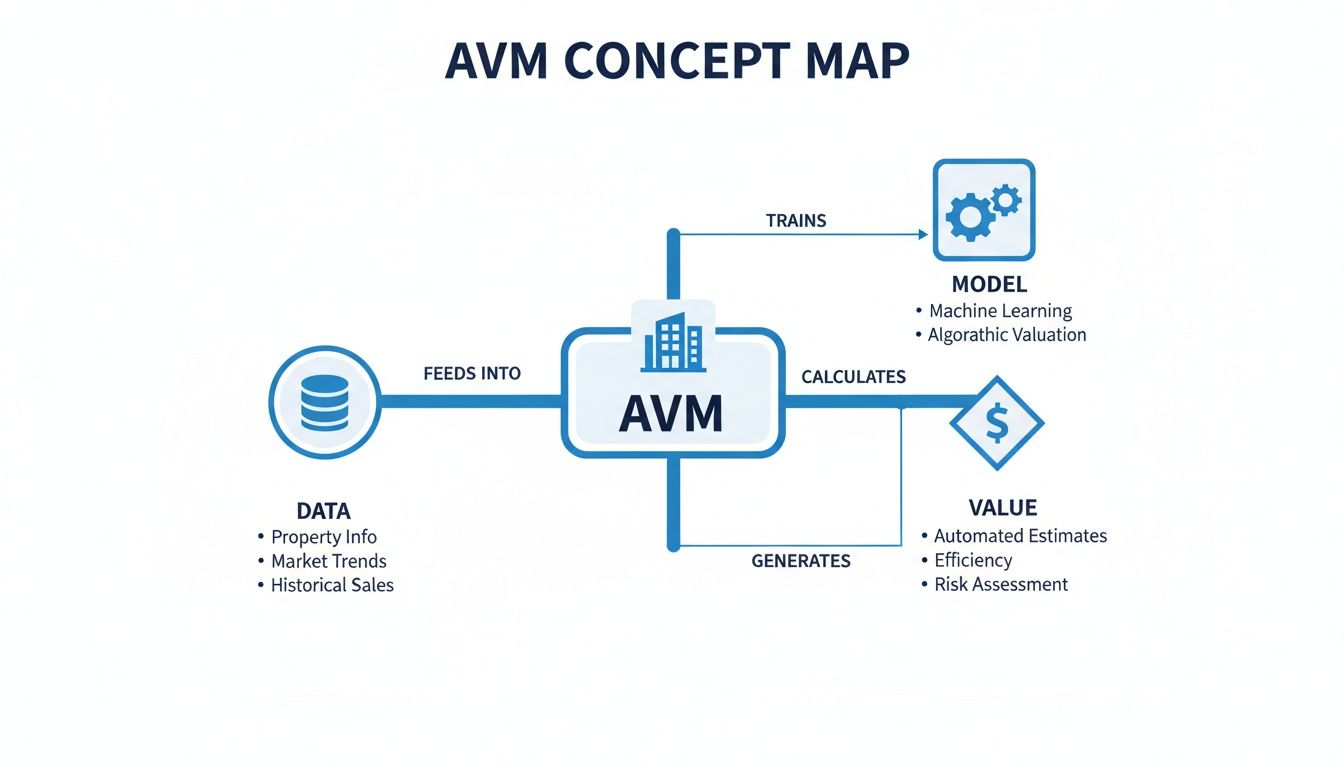
An Automated Valuation Model (AVM) is a software algorithm that calculates a property's market value using data and statistical models. If you have ever used an online tool to get an instant "value estimate" for a property, you have used an AVM.
The International Association of Assessing Officers (IAAO) defines AVMs as mathematically based programs that analyze property details, market trends, and location data. By automating this process, they eliminate the time and expense of a manual appraisal for initial assessments, answering the question: What is this property likely worth today?
How Do Real Estate AVMs Work?
An Automated Valuation Model operates as a data analyst, processing a collection of data points that represent a house and its place in the market. It processes massive datasets from numerous sources, identifies patterns, and applies complex mathematical formulas to produce an estimated value.
AVMs are the core technology behind most modern real estate platforms, providing investors, agents, and lenders with instant home values. The process is not a single calculation but a system that converts raw data into a final valuation.
Sophisticated algorithms interpret this data, and understanding their mechanics reveals the strengths and weaknesses of any AVM estimate.
Core Modeling Engines
Two primary modeling approaches perform most of the analysis.
- Hedonic Models: This model is built on the premise that a property's value is the sum of its individual features. It analyzes how specific attributes—like a renovated kitchen, an additional bathroom, or a top-rated school zone—impact the final sale price, assigning a dollar value to each attribute.
- Repeat-Sales Indices: This method focuses on market momentum by tracking the price changes of the same properties as they sell and resell over time. This makes it highly effective at measuring broad market appreciation or depreciation in a specific area.
The most effective AVMs use a hybrid model. This approach blends the granular detail of hedonic models with the market-trend accuracy of repeat-sales data. Layering on machine learning allows the model to improve over time as new sales data becomes available. Adding location data further refines the valuation, demonstrating how geospatial analysis enhances automated valuation models.
How Accurate Are AVMs?
The accuracy of an Automated Valuation Model depends on the property type and the quality of the input data. An AVM is not intended to replace an appraiser for a unique historic property that requires a physical inspection.
For tasks like analyzing an entire portfolio, screening hundreds of potential deals, or monitoring property values at scale, the AVM's speed and low cost are superior. It is about using the right tool for the job.

AVM vs. Appraisal vs. CMA
This table compares AVMs against the two other primary methods of property valuation: the formal appraisal and the real estate agent’s Comparative Market Analysis (CMA).
| Factor | AVM (Automated Valuation Model) | Appraisal | CMA (Comparative Market Analysis) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost | $5 – $50 per property | $400 – $800+ | Typically Free (from an agent) |
| Speed | Instant (seconds) | 5-10 business days | 1-2 days |
| Data Inputs | Public records, MLS data, market trends | On-site inspection, public records, comps | Active and sold MLS listings, agent expertise |
| Best Use Case | Portfolio analysis, loan pre-qualification, lead generation | Mortgage lending, legal disputes, complex properties | Setting a listing price, making an offer |
The choice of tool depends on the required speed, cost, and level of scrutiny. For instant, scalable data-driven insights, AVMs are the optimal choice.
Key AVM Accuracy Metrics
Professional-grade AVMs provide metrics to gauge their reliability. The two most important are the confidence score and the Forecast Standard Deviation (FSD).
- A confidence score is a rating (e.g., 1-5 stars or 1-100) indicating the model's certainty about its valuation. A high score signifies the property fits a predictable pattern and multiple algorithms produced a similar value.
- The Forecast Standard Deviation (FSD) is a statistical measure of precision that provides a probable value range. An AVM value of $300,000 with an FSD of 0.10 (10%) means there is a 68.3% probability the property's true market value is between $270,000 and $330,000. A lower FSD indicates a tighter range and a more reliable estimate.
Our deep-dive guide explains more about how AVMs use accuracy benchmarks for better valuations.
Who Uses AVMs in Real Estate?
An Automated Valuation Model is a functional tool that powers major operations across the real estate industry. Its core function is efficiency, enabling professionals to sift through thousands of properties to identify those that fit a specific financial model.
Mortgage Lenders and Servicers
Lenders use AVMs for risk management. For initial underwriting on lower-risk loans, such as certain refinances or home equity lines of credit (HELOCs), an AVM provides a reliable valuation checkpoint without the time and expense of a full appraisal.
AVMs are also critical for monitoring existing loan portfolios. Lenders run AVMs across their entire book of business quarterly to monitor collateral value shifts in near real-time, flagging properties where the loan-to-value (LTV) ratio is increasing. This functions as an early warning system to identify potential risks before a borrower defaults.
Real Estate Investors
For an investor, an AVM is a filtering tool. An investor using a platform like BatchData can analyze an entire county's worth of properties in seconds. They can set specific filters, such as identifying homes where the AVM-estimated value is significantly higher than the last sale price, instantly flagging properties with high appreciation potential.
For example, an investor could search for all properties in a zip code with an estimated 30% or more equity and a high AVM confidence score. This query creates a targeted list of potential off-market deals, allowing them to focus marketing resources on homeowners most likely to be receptive to an offer.
Proptech and Real Estate Tech
Proptech companies are built on data, and for many, AVMs are their core engine. The "instant home value" estimators on major real estate portals are powered by AVMs, attracting millions of users.
These companies integrate AVMs into their platforms via APIs to deliver property valuations directly within their applications. AVMs are also a key component in the ecosystem of AI tools for real estate agents, supporting functions from marketing to lead follow-up.
What Are the Limitations of AVMs?
An Automated Valuation Model's greatest strength—relying purely on data—is also its biggest weakness. An AVM cannot physically inspect a property or assess its unique character.
This creates significant blind spots. AVMs often struggle with unique properties, like historic homes or custom architectural designs, due to a lack of comparable data. They also lose accuracy in rural areas where sales are infrequent, forcing the algorithm to use outdated data.

The "Garbage In, Garbage Out" Problem
The accuracy of any AVM is determined by the quality of its input data. If public records are outdated, incomplete, or incorrect, the valuation will reflect these flaws. This is the "garbage in, garbage out" principle.
An AVM does not account for a property's interior condition. It will not factor in a $75,000 kitchen remodel or, conversely, major undocumented structural damage. For this reason, an AVM is best used as a starting point for analysis or a tool for assessing portfolio risk, not as a replacement for a full appraisal when stakes are high.
How Does BatchData Enhance AVMs for Professionals?
A professional-grade data solution provides the context behind the AVM number. BatchData transforms a simple AVM from a standalone estimate into a strategic asset by integrating it into a complete property data ecosystem.
We enrich our AVMs with over 1,000 additional property attributes to create a full financial and situational picture of the asset.
Beyond the Valuation
Professionals require actionable intelligence. We deliver this by layering critical data points on top of the core AVM value.
- Financial Health: Instantly view a property’s complete mortgage history, including original loan amounts, lender details, and active liens.
- Distress Signals: Identify risk and opportunity indicators like pre-foreclosure status, tax delinquencies, or recent bankruptcy filings.
- Owner Intel: Access verified owner contact information, including phone numbers and emails, to facilitate direct marketing.
This unified data—delivered via a low-latency API or in bulk files—enables sophisticated underwriting, proactive portfolio monitoring, and highly targeted marketing campaigns. By integrating these elements, you understand not only what a property is worth but, more importantly, why.
You can learn more about the specifics in our detailed overview of the BatchData Automated Valuation Model.
What Are Common Questions About AVMs?
These are frequently asked questions about using an Automated Valuation Model (AVM) with direct answers.
Are Zestimates and other online estimators AVMs?
Yes. Consumer-facing tools like Zillow's Zestimate are the most well-known type of AVM.
However, a significant difference exists between these public-facing tools and the enterprise-grade AVMs used by professionals. Tools from BatchData pull from more comprehensive and timely datasets and provide detailed confidence scores and accuracy metrics not available in free versions. While the core technology is similar, the data depth and precision are engineered for professional risk assessment.
How often should I check an AVM value?
This depends on your strategy and market conditions. For active investors or lenders managing a portfolio, quarterly checks are a best practice to monitor asset value.
In a volatile market, monthly checks may be necessary to stay ahead of significant shifts. A dynamic data platform like BatchData, which offers daily data updates, allows for near real-time value monitoring when conditions are uncertain.
Can an AVM be used to challenge property taxes?
An AVM is a starting point for research, but it is not sufficient evidence for a tax appeal. Most tax assessment authorities require a formal appraisal or a detailed Comparative Market Analysis (CMA). A proper CMA involves manually selecting the most relevant comparable sales to build a case, which is a step beyond what an automated model can provide.
Ready to move beyond basic estimates? See how BatchData integrates AVMs with thousands of other data points to give you the complete property picture. Explore our data platform today.