SEO Title: Real Estate Valuation Software: A Data-Driven Guide
SEO Meta Description: Explore how real estate valuation software works, its key applications for lenders and investors, and how to choose the right vendor for your business.
SEO Meta Keywords: real estate valuation software, automated valuation model, AVM software, property valuation, real estate data, proptech
Using real estate valuation software is the difference between guessing a property's worth and knowing it with data. It’s a platform that uses algorithms and massive datasets to calculate a property's value almost instantly, replacing slow, manual appraisals with high-speed, objective analysis. This technology is now the standard for mortgage underwriting, investment analysis, and portfolio management, delivering data-driven valuations at a scale previously thought impossible.
| Core Takeaway | Description |
|---|---|
| Speed & Scale | Replaces manual appraisals that take weeks with instant, algorithmic valuations. |
| Core Technology | Driven by Automated Valuation Models (AVMs) that analyze millions of data points. |
| Primary Users | Mortgage lenders, institutional investors, iBuyers, and insurance carriers. |
| Key Metric | Accuracy is measured by Median Absolute Percentage Error (APE), typically 2-6% in active markets. |
This shift to automated analysis is the definitive future of property technology, enabling faster, more accurate decisions across the entire industry.
What is Modern Property Valuation?
Modern real estate valuation software is a quantitative tool that provides an immediate, data-backed answer to the fundamental question: What is this property worth right now? The core of this technology is the Automated Valuation Model (AVM), an algorithm that processes millions of data points—property records, market trends, comparable sales—in seconds to produce a valuation.
This is a direct response to the industry's demand for speed, consistency, and objective evidence, particularly for high-volume portfolio management. The global real estate software market was valued at USD 12.86 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit USD 38.33 billion by 2033, growing at a 12.9% CAGR. This growth signals a fundamental industry-wide reliance on digital tools. For more context, see these market trends and the digital shift in real estate.
The Problem It Solves
The traditional appraisal process is the primary bottleneck. It requires a licensed appraiser to physically visit a site, research comparable sales (comps), and produce a lengthy report. This manual method is slow (weeks), costly (hundreds of dollars per property), and inconsistent due to subjective judgment. Valuation software directly eliminates these obstacles.
Modern Valuation vs. Traditional Appraisal
| Attribute | Valuation Software (AVM) | Traditional Appraisal |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Instant to minutes | Days to weeks |
| Cost | A few dollars per property, or less at scale | Hundreds of dollars per property |
| Scalability | Thousands of properties simultaneously | One property at a time |
| Data Source | Aggregated public records, MLS data, market trends | Appraiser research, local knowledge, physical inspection |
| Objectivity | Highly objective, algorithm-based | Potentially subjective |
| Primary Use Case | Portfolio monitoring, initial underwriting, investment screening | Final loan approval, complex properties, legal disputes |
Key Applications
An Automated Valuation Model (AVM) is the engine behind the software, powering several critical business functions:
- Mortgage Origination: Lenders use AVMs for rapid pre-qualification and home equity loan underwriting.
- Portfolio Monitoring: Institutional investors and banks use AVMs to revalue large real estate portfolios in real time, managing risk and equity.
- Investment Analysis: Real estate investors and iBuyers use AVMs to screen potential acquisitions and generate instant offers at scale.
- Consumer-Facing Tools: Real estate portals like Zillow use their "Zestimate" AVM to engage users and generate leads.
This software isn't about replacing appraisers; it's about augmenting their work and handling high-volume, standardized valuations with unprecedented efficiency.
How do Automated Valuation Models Work?
The engine inside all real estate valuation software is the Automated Valuation Model (AVM). The AVM is a statistical model that analyzes vast property datasets to calculate an objective, data-driven estimate of a property's market value, removing human subjectivity and manual labor from the process.
This diagram illustrates the fundamental flow: raw data is ingested, the AI model processes it, and a usable property valuation is the output.
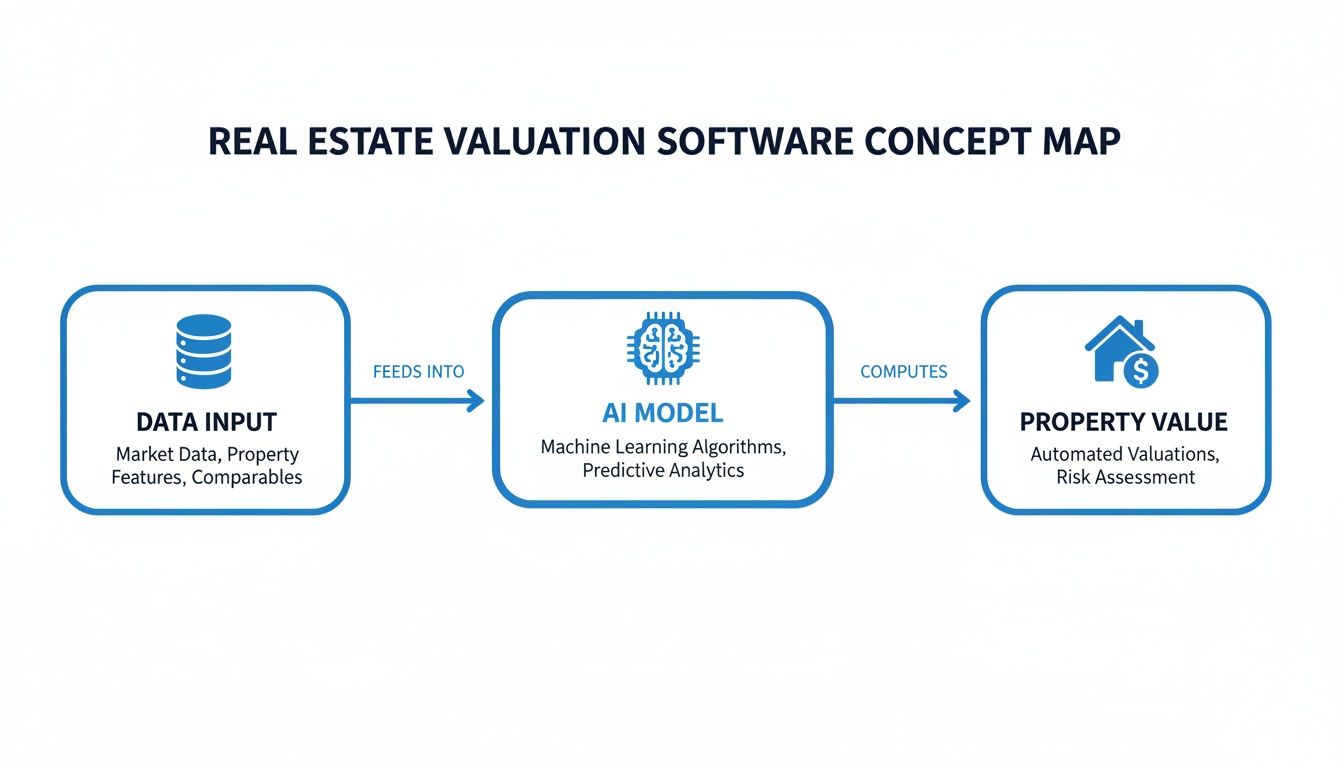
Valuation Model Types
AVMs are not one-size-fits-all; different models solve different problems based on available data and the specific valuation goal.
- Hedonic Models: The classic AVM. It deconstructs a property into its core attributes—square footage, bedrooms, bathrooms, lot size—and assigns a monetary value to each. This model can quantify the value added by specific features, like a renovated kitchen.
- Repeat-Sales Models: These models track market trends by analyzing the price change of the same property over multiple sales. This creates a price index that clearly shows market appreciation or depreciation over time.
- Machine Learning Models: The most advanced AVMs. These use complex algorithms like gradient boosting and neural networks to identify non-linear patterns in data that simpler models would miss. For a primer, see this guide on machine learning for businesses and AI integration.
Automated Comparable Selection
Finding relevant "comps" (comparable properties) is foundational to valuation. An AVM automates this by sifting through thousands of potential comps in milliseconds, applying precise, rule-based adjustments for differences in size, age, or condition. This eliminates the human bias inherent in manual selection and ensures consistent, defensible valuations. For example, if a comp has an extra bathroom, the AVM applies a data-backed adjustment based on that feature's market value, a level of precision impossible to achieve manually at scale. The best models also incorporate hyperlocal data, a concept detailed in this guide on how geospatial analysis enhances automated valuation models.
Model Validation and Accuracy
An AVM's credibility depends on proven accuracy. This is established through model validation and backtesting, where the model is rigorously tested against historical sales data.
The process is straightforward:
- Model Training: The AVM analyzes a large dataset of past property sales to "learn" value drivers.
- Backtesting: The model generates valuations for a separate, "unseen" set of historical sales where the actual sale price is known.
- Error Measurement: The AVM's predicted value is compared against the actual sale price to calculate the error.
- Confidence Calculation: Key metrics are derived, primarily the Median Absolute Percentage Error (APE). A low APE, typically in the 2-6% range for active markets, indicates a highly accurate model and results in a "confidence score" that signals the valuation's reliability.
How is Technical and Data Integration Handled?
Integrating real estate valuation software into your business workflows requires a clear technical strategy. The most efficient and flexible method for real-time data integration is via an Application Programming Interface (API). An API acts as a digital conduit, allowing your software to request a property valuation from a vendor's platform and receive a structured, machine-readable response in milliseconds.

Real-Time API Valuations
An API integration provides on-demand access to property values without the burden of storing or managing the underlying datasets.
- iBuyer Platforms: When a homeowner requests an offer, the platform's engine pings an API for a real-time AVM, which forms the basis of the instant offer.
- Mortgage Pre-Qualifiers: A lender's online portal uses an AVM API to instantly check a property's estimated value during an application.
- Real Estate Portals: Home value estimators on property websites make continuous API calls to serve fresh valuations for millions of properties.
For these applications, performance is non-negotiable. Critical metrics include API latency (response time) and uptime (service reliability). A delay of even a few hundred milliseconds can degrade the user experience and halt operations.
Bulk Data Delivery
For portfolio-wide analysis, training custom machine learning models, or deep market research, bulk data delivery is the appropriate method. Instead of requesting valuations one-by-one, you receive a complete dataset containing millions of property records. This enables deep, offline analysis where your data science team can merge the vendor's valuation data with your internal records to build proprietary risk models.
Delivery options typically include:
- Flat Files: Data is delivered in standard formats like CSV or Parquet via a secure file transfer protocol (SFTP).
- Cloud Data Warehouses: Data is synced directly into your cloud environment, such as Amazon S3 or Snowflake, simplifying data engineering.
The quality of this data is paramount, as detailed in our guide on how multi-source data enhances automated valuation models.
Data Security and Compliance
All property data integrations must adhere to strict security protocols. Property data often contains sensitive information, making data security and compliance mandatory. A vendor must demonstrate adherence to industry standards, including data encryption both in transit (over the internet) and at rest (on servers). Compliance with data privacy laws like CCPA is also critical. A data breach carries significant financial and legal consequences.
Who Uses Real Estate Valuation Software?
Real estate valuation software is foundational technology for any enterprise requiring speed, scale, and objectivity in property analysis. The core value is replacing slow, subjective manual work with automated, data-driven intelligence to manage risk and capitalize on opportunities.
Mortgage Lenders and Servicers
Mortgage lenders are the primary users of automated valuation data. In a high-volume, low-margin industry, speed and accuracy are directly tied to profitability and regulatory compliance.
- Loan Origination: Lenders use AVMs for instant pre-qualification and for underwriting low-risk products like home equity loans and refinances. This reduces appraisal costs and shrinks loan approval timelines from weeks to days.
- Portfolio Risk Management: Lenders and servicers use AVMs to revalue their entire loan portfolios quarterly. This provides an up-to-date assessment of loan-to-value (LTV) ratios and overall risk exposure.
Institutional Investors and iBuyers
Institutional investors, hedge funds, and iBuyers depend on this software to operate at a scale previously impossible. Their business models are built on making thousands of data-driven acquisition decisions rapidly.
- iBuyers: Companies like Opendoor and Offerpad use AVMs as the core of their instant offer engines. An AVM provides the baseline valuation in seconds, allowing for the generation of a preliminary cash offer.
- Single-Family Rental (SFR) Investors: These firms use bulk AVMs to screen thousands of listings across multiple markets simultaneously, instantly identifying undervalued assets that meet their investment criteria.
The real estate investment software market is projected to reach USD 3.0 to USD 6.0 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of up to 15.0% through 2030, driven by the demand for data aggregation and real-time asset performance analysis. You can find more details in this real estate investment software market report.
Proptech Platforms and Real Estate Portals
Consumer-facing real estate platforms use AVMs as a powerful user acquisition and lead generation tool. Instant home value estimates attract homeowners and potential sellers. Major portals like Zillow use their proprietary AVM—the "Zestimate"—to provide a value estimate on nearly every home in the U.S., which serves as a conversation starter between consumers and real estate agents.
Insurance Carriers
The insurance industry uses valuation software to calculate replacement cost. Before underwriting a homeowners insurance policy, carriers need a precise estimate of what it would cost to rebuild a property. Automated models calculate this by analyzing granular property data, local construction labor rates, and material costs, ensuring policies are priced correctly and homeowners are adequately covered.
How do you Select a Valuation Software Vendor?
Choosing the right real estate valuation software is a strategic decision that directly impacts operational efficiency and profitability. Your evaluation process must be data-driven, focusing on the quality and performance of the underlying data and models, not just the user interface. Before starting, it is useful to review a comprehensive 'build vs buy' software decision framework to clarify your internal strategy.
Core Evaluation Criteria
Your evaluation must focus on three pillars: data accuracy, technical performance, and operational support. Demand complete transparency from any potential vendor.
- Median Absolute Percentage Error (APE): The primary accuracy metric. A top-tier vendor should demonstrate a median APE below 5% in major metropolitan statistical areas (MSAs).
- Forecast Standard Deviation (FSD): Measures the consistency of the AVM's predictions. A low FSD indicates stable and reliable valuations.
- Hit Rate: The percentage of properties for which the vendor can generate a valuation. A low hit rate indicates significant gaps in data coverage.
The AVM is only as good as its underlying data. Understanding how to choose the best real estate data provider for your business is a critical prerequisite.
Running a Pilot Program
Never accept a vendor’s accuracy claims without verification. The only way to confirm performance for your assets in your markets is by running a controlled pilot program.
- Prepare a Holdout Sample: Create a list of 200-500 properties from your portfolio with known recent sales prices. This is your ground truth.
- Submit for Valuation: Provide the vendor with only the property addresses and request AVM results.
- Compare Results: Measure their AVM values against your known sales prices to calculate their real-world median APE.
- Analyze Outliers: Investigate properties where the AVM was highly inaccurate to identify the model's blind spots (e.g., unique properties, specific submarkets).
A pilot program is the most effective form of due diligence, replacing marketing claims with hard data before you sign a contract.
Vendor Evaluation Checklist
| Evaluation Category | Key Questions | Ideal Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Data & AVM Accuracy | What is your median APE by MSA? How frequently are your data feeds refreshed? | Median APE under 5%; daily or weekly data refresh cycles. |
| Technical Performance | What is your average API latency? Can you provide uptime statistics for the last 12 months? | Latency under 500ms; guaranteed uptime of 99.9% or higher. |
| Integration & Support | Is your API documentation public and well-maintained? What is your technical onboarding process? | Clear, comprehensive documentation with code samples; dedicated integration support. |
| Cost & Scalability | What are your pricing models (per-call, subscription)? Are volume discounts available? | Transparent, flexible pricing that scales with usage. |
What is the Implementation Framework?
Implementing real estate valuation software is a strategic project, not a simple technical task. A successful implementation requires a clear roadmap that connects the technology directly to measurable business goals, ensuring a tangible return on investment. Vague goals like "improve efficiency" are insufficient. Define specific outcomes, such as "reduce mortgage underwriting time by 25%" or "increase weekly investment screenings by 400%."

The Integration Process
A successful rollout follows a phased sequence. Rushing or skipping steps is the primary cause of implementation failure.
- Scope Technical Integration: Engineers create a technical plan, setting up API keys, defining data schemas, and mapping vendor data fields to internal systems.
- Run a Controlled Pilot: Test the AVM's performance against a known set of properties to validate accuracy and identify any regional weaknesses.
- Embed API Calls: Integrate the API calls directly into existing software workflows, such as a loan origination system or an investment analysis platform.
- Train Team and Rollout: Train end-users (underwriters, analysts) on how to interpret the data, particularly confidence scores. A phased rollout starting with a small group of power users is recommended.
Common Implementation Pitfalls
Several common mistakes can derail an implementation. The property tech industry is rapidly adopting data-driven tools—the property management software market, valued at USD 3.23 billion in 2024, is projected to hit USD 5.12 billion by 2032. Getting this right is critical. Learn more about the accelerating adoption rates in property tech.
The single biggest pitfall is treating an AVM value as absolute truth. It is a powerful, data-driven estimate, not a perfect prediction.
- Misinterpreting Confidence Scores: A low confidence score is a signal for caution, not a model failure. It indicates the property may be unique or lack sufficient comps, suggesting a manual review is necessary.
- Ignoring Regional Accuracy Variations: An AVM that performs well in a dense urban market may struggle in a rural area with sparse data. Always demand accuracy metrics broken down by geography.
- Failing to Monitor Model Drift: Market conditions change. A model's accuracy can "drift" if not continuously retrained with fresh sales data. Ensure your vendor has a rigorous process for ongoing model validation.
Frequently Asked Questions
How accurate is this software compared to a human appraiser?
High-quality real estate valuation software is highly accurate, typically achieving a Median Absolute Percentage Error (APE) within 2-6% of the final sale price in active markets. However, an algorithm cannot see a custom kitchen renovation or identify foundation issues. A human appraiser excels at capturing unique, on-the-ground context. The best approach is a hybrid model: use software for speed and scale, and deploy human appraisers for complex, high-value, or unique assets requiring nuanced judgment.
Can this software value commercial real estate?
Generally, no. Most AVMs are designed and trained specifically for residential properties. Commercial real estate (CRE) valuation is a different discipline, driven by income-generating potential (e.g., capitalization rates, net operating income, discounted cash flow), not just sales comps. CRE valuation requires specialized platforms that analyze lease data, tenant risk profiles, and local income trends.
What is the typical pricing model for these APIs?
Pricing models vary, but typically fall into one of three structures:
- Pay-Per-Call: You are charged for each successful API request.
- Tiered Subscriptions: A flat monthly fee for a set number of API calls.
- Enterprise Contracts: Custom pricing for high-volume or bulk data usage.
The cost per valuation can range from a fraction of a cent to several dollars, depending on data depth, volume, and the specific vendor. The optimal model depends on whether your workflow requires on-demand valuations or large-scale portfolio analysis.
Ready to power your operations with the most accurate property data available? BatchData provides comprehensive property records, AVMs, and verified owner contacts through flexible, low-latency APIs and bulk delivery. Explore our data solutions today.
Article created using Outrank



