When managing real estate data, you have two main options: trigger-based updates or batch updates. Trigger-based systems send real-time notifications whenever specific changes occur, like new listings or price drops, helping you act immediately. Batch updates, on the other hand, collect and deliver large datasets on a fixed schedule (e.g., daily or monthly), making them better suited for tasks like market analysis or CRM updates.
Key Takeaways:
- Trigger-Based Updates: Ideal for time-sensitive tasks like lead generation and fraud detection. They offer immediate alerts but require complex infrastructure.
- Batch Updates: Best for handling large volumes of data, such as market reports or bulk data enrichment. They’re cost-effective but may lag behind real-time changes.
Quick Comparison:
| Feature | Trigger-Based Updates | Batch Updates |
|---|---|---|
| Timing | Real-time | Scheduled |
| Use Cases | Lead alerts, fraud detection | Market analysis, CRM updates |
| Scalability | High-frequency events | Large datasets |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Infrastructure | Complex | Simpler |
Combining both approaches can maximize efficiency: use triggers for immediate actions and batch updates for large-scale tasks.
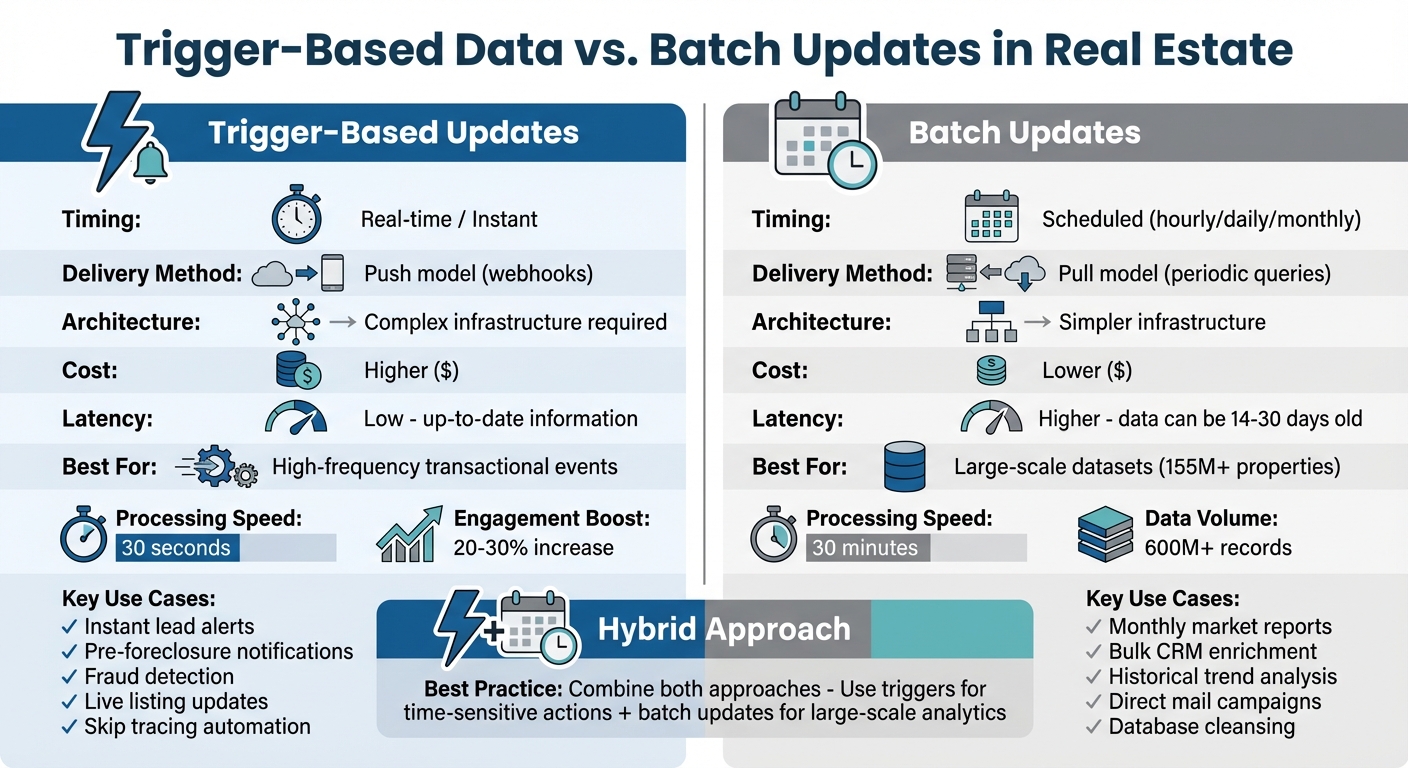
Trigger-Based vs Batch Updates in Real Estate: Complete Comparison
Real Estate End to End Data Engineering using AI
sbb-itb-8058745
What Are Trigger-Based Data Updates?
Trigger-based updates rely on an event-driven "push" system where data automatically flows from the source – like an MLS database – to your platform as soon as a change happens. Instead of relying on periodic polling, updates are sent instantly when key events occur, such as new property listings, price changes, status updates (e.g., "Active" to "Sold"), or adjustments to media or open house schedules.
These updates utilize webhooks, which deliver event details through an HTTP POST request in real time. Paired with Change Data Capture (CDC) – a method that tracks INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE operations in database logs – this setup ensures no changes go unnoticed. A typical configuration includes:
- Event Listener: Detects database changes.
- Dispatcher: Queues and sends events.
- Subscription Manager: Allows clients to subscribe to specific event types.
"The moment a property in our national database matches your profile, we instantly push that event to you via a webhook or direct integration. This isn’t a list; it’s a real-time stream of opportunities."
– BatchData
This approach eliminates inefficiencies by processing only relevant updates. Efforts like those from the Real Estate Standards Organization (RESO) aim to standardize webhooks across MLS providers, further enhancing compatibility and the advantages of this event-driven model.
Benefits of Real-Time Data Processing
The architecture behind trigger-based updates explains why they deliver unmatched speed and responsiveness in real estate data. Instant notifications give agents and investors a competitive edge in fast-moving markets. Whether it’s a price drop or a status change, the system alerts users within seconds, enabling quick action. This immediacy helps automate lead generation, keeps CRM systems updated, and ensures marketing campaigns and analytics reflect the latest market conditions.
Efficiency is another key advantage. Log-based CDC reads transaction logs with minimal impact on system performance. For platforms managing millions of property records, transitioning from polling to this push-based model reduces server load and improves processing speed. However, while CDC ensures rapid updates, it also requires strong error-handling and synchronization mechanisms to maintain data accuracy.
Challenges of Trigger-Based Systems
Despite the benefits, implementing trigger-based systems comes with its own set of challenges. Building components like listeners, dispatchers, and secure subscription management (e.g., HMAC signature verification) demands a more complex infrastructure compared to simpler batch processing. Your system must also handle sudden spikes in data traffic during peak times.
Data consistency is another hurdle. Since webhooks typically deliver only the changes (deltas) rather than the full dataset, downstream systems need robust synchronization logic to apply updates correctly. If a webhook fails – due to network issues or downtime – critical updates could be missed without retry mechanisms or fallback reconciliation. Additionally, when using CDC, monitoring replication lag is crucial. Unprocessed transaction logs can pile up, potentially overwhelming storage if not managed efficiently.
What Are Batch Updates?
Unlike push-based trigger updates that send notifications instantly, batch updates operate on a schedule. At regular intervals – like hourly, daily, or weekly – your system queries the database to check for new data. Instead of real-time notifications, this approach delivers aggregated data snapshots, often as CSV files. These files are typically sent to cloud storage platforms like Amazon S3, Google Drive, or transferred via SFTP.
This method is particularly suited for tasks where immediate action isn’t required. For example, real estate teams frequently rely on batch processing for skip tracing (uploading lists to enrich contact information), standardizing addresses to meet USPS guidelines, or ensuring CASS certification for direct mail campaigns.
"Traditional real estate data APIs operate on a ‘pull’ model. You have to constantly poll their system, asking ‘Is there anything new yet?’ over and over. This is inefficient, costly, and slow." – BatchData
The defining feature of batch updates is their static nature. Each dataset represents a snapshot frozen at a specific moment. Once downloaded, the data begins to age. While trigger-based systems push updates as they happen, batch updates may lag hours or even days behind. For workflows like historical reporting, market analysis, or enriching large datasets, this delay is acceptable. In such cases, the focus on data volume and completeness outweighs the need for real-time accuracy.
Benefits of Scheduled Data Updates
Batch processing shines in scenarios where handling large data volumes is more important than instant updates. For tasks like address cleansing, geocoding, or enriching extensive property datasets, scheduled jobs are a practical solution. Take BatchData, for instance – it provides access to over 600 million records covering addresses, property details, and phone numbers, making it well-suited for high-volume operations.
Another advantage is its cost efficiency. Pay-as-you-go models allow businesses to process data only when needed, avoiding fixed subscription fees during slower periods. This flexibility is especially helpful for non-technical users, as automated file deliveries can seamlessly integrate with tools like Excel, CRM platforms, or marketing software without requiring complex setups.
Batch updates are also ideal for compliance and historical analysis. For example, address validation ensures mailing lists meet USPS standards before launching campaigns. Tools like Delivery Point Validation (DPV) and CASS Certification help verify thousands of addresses at once. Similarly, when generating quarterly market reports or analyzing long-term trends, the slight delay in data freshness is a small price to pay for the efficiency and scale batch processing offers. While it may not match the immediacy of real-time systems, it effectively supports compliance-driven and large-scale analytical tasks.
Limitations of Batch Updates
The main downside of batch updates is data latency. Since the process relies on past data, you’re always reacting to outdated information. For instance, by the time a scheduled query identifies a high-equity property or pre-foreclosure opportunity, competitors using real-time systems might already have acted. This risk grows as the interval between updates increases – a property listed as "Active" in the morning batch might already be under contract by noon, with no way for your system to reflect this until the next update.
Additionally, the pull model’s repetitive polling wastes resources, as the system continuously checks for updates even when no changes occur. Batch processing can also limit operational flexibility; static snapshots may not meet the demands of workflows requiring immediate responses or constant updates.
Trigger-Based Data vs. Batch Updates: Key Differences
When it comes to updating data, the main difference between trigger-based and batch updates lies in their timing and method of delivery. Trigger-based updates send out instant notifications whenever an event occurs, while batch updates gather and deliver aggregated data on a set schedule.
One key point to remember is that network latency and database latency are not interchangeable. For example, a batch system might return an API response in milliseconds, suggesting low network latency. However, the underlying data could be outdated – sometimes by as much as 30 days, especially in monthly cycles where the average data age is around two weeks.
"The distinction between ‘fast API response’ and ‘fresh data’ is not semantic – it’s the difference between winning and losing deals." – Crustdata
This difference in architecture significantly impacts both efficiency and cost. Trigger-based systems operate on a push model, delivering updates as soon as specific conditions are met. In contrast, batch systems rely on a pull model, periodically retrieving updates, which can lead to delays.
When it comes to scalability, batch processing shines with large datasets – think machine learning models handling over 155 million records. On the other hand, trigger-based systems are better suited for high-frequency transactional events, such as tracking pre-foreclosure status updates. These distinctions help define which method works best for specific real estate data needs.
Comparison Table: Trigger-Based vs. Batch Updates
Here’s a quick summary of the differences:
| Feature | Trigger-Based Updates | Batch Updates |
|---|---|---|
| Timing | Immediate; occurs as soon as a change is detected | Scheduled; occurs at defined intervals |
| Latency | Low database latency; up-to-date information | Higher latency; data may be up to 30 days old |
| Scalability | Ideal for high-frequency, transactional events | Great for processing large-scale datasets |
| Use Cases | Real-time lead alerts, fraud detection | Market analysis, CRM pre-population, machine learning training |
| Architecture | Push model (e.g., webhooks, synchronous API) | Pull model (e.g., ETL pipelines, bulk API endpoints) |
| Data Volume | Best for specific records or changes | Best for nationwide/complete datasets (155M+ properties) |
| Error Handling | Requires advanced engineering for resilience | Simpler; failed jobs can be retried without live user impact |
Each method has its strengths, so choosing the right one depends on your specific data needs and operational priorities.
Pros and Cons of Each Approach
Trigger-based and batch updates each come with their own strengths and weaknesses, shaping how real estate platforms manage data. By weighing these trade-offs, you can craft a strategy that balances timely updates with large-scale analytics. This understanding can guide you toward the right approach – or even a mix of both.
Pros and Cons of Trigger-Based Updates
Trigger-based updates offer real-time advantages by immediately pushing data as it changes. However, these systems demand a more advanced infrastructure. Here’s a closer look:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Instant Lead Alerts: Sends updates to investors as soon as a property meets specific criteria, such as entering pre-foreclosure. | Increased API Calls: Every update triggers a request, potentially raising costs and adding strain to systems. |
| Up-to-Date Accuracy: Keeps pricing and availability current, avoiding outdated snapshots. | Complex Infrastructure: Requires webhooks, event brokers, and advanced error management to handle real-time data streams effectively. |
| Improved Local SEO: Ensures listing consistency across search engines and directories. | Limited Third-Party Support: Some platforms don’t support real-time updates, limiting integration options. |
| Dynamic Workflows: Automatically updates CRMs or marketing systems without manual input. | Advanced Engineering Required: Managing rate limits, asynchronous callbacks, and variable latency demands specialized expertise. |
| Time Efficiency: Reduces processing time from 30 minutes to just 30 seconds. | Overkill for Some Use Cases: May not justify premium costs for tasks like basic research or historical analysis, where real-time data isn’t critical. |
Pros and Cons of Batch Updates
Batch updates are ideal for cost-effective processing of large datasets but come with lag times that may hinder quick decision-making. Here’s how they stack up:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Cost-Effective Enrichment: Processes bulk data at a lower cost per record. | Stale Information: Monthly cycles can leave data 14 to 30 days old, creating gaps in intelligence. |
| Scales Well for Large Datasets: Perfect for analyzing market trends. | Missed Opportunities: Competitors using real-time updates may act on deals before your batch data is refreshed. |
| Lower Operational Overhead: Fewer API calls simplify monitoring and reduce system strain. | Longer Time-to-Update: Delays in reflecting changes can slow critical business decisions. |
| Simpler Error Handling: Failed batches can be retried without affecting live users or causing application crashes. | Reactive Strategy: As BatchData puts it, "By the time your query finds a property, the data is already aging and the competition is already moving". |
| Legacy Compatibility: Works seamlessly with traditional systems, making integration straightforward. | Inaccurate Personalization: Outdated data can lead to errors, like contacting buyers about properties that are already sold, harming credibility. |
Many real estate platforms now combine these methods in a hybrid "waterfall" strategy. For instance, they might use trigger-based updates for time-sensitive data like price changes, while relying on batch updates for less urgent, large-scale data. This approach strikes a balance between immediacy and cost efficiency.
The next section will explore specific real estate scenarios to show how these approaches can be applied effectively.
Use Cases in Real Estate
When to Use Trigger-Based Data Updates
Trigger-based systems shine in scenarios where timing is everything. For example, when a property enters pre-foreclosure or meets specific criteria like high equity and absentee ownership, investors can receive instant notifications via webhooks. This push-based model eliminates the delays of traditional polling, giving you a head start in making contact.
These updates also streamline processes like skip tracing. Verified contact details are appended to leads the moment they’re captured, enabling immediate outreach. As Chris Finck, Director of Product Management at BatchData, puts it: "What used to take 30 minutes now takes 30 seconds".
Fraud and risk monitoring also benefit from real-time updates. Trigger-based systems can flag active liens, mortgage changes, or pre-foreclosure filings instantly, providing a financial snapshot of a property before you commit. Similarly, live listing updates ensure buyers and agents are always informed about status changes like "Pending" or "Sold", avoiding wasted efforts on properties no longer available.
Even home service companies can leverage this technology for targeted marketing. For instance, if a property’s roof is over 15 years old or a new pool permit is filed, automated systems can send tailored offers to homeowners at the perfect moment.
When to Use Batch Updates
While trigger-based updates are great for immediate actions, batch updates excel in large-scale, less time-sensitive tasks. For instance, monthly market reports that aggregate sales data, price trends, and inventory statistics provide insights into broader patterns over weeks or months, rather than requiring real-time data.
Batch updates are also ideal for bulk data enrichment. Enhancing thousands of CRM records with additional details like demographics, school ratings, or crime statistics is more cost-effective when processed in bulk. This approach is often favored for direct mail campaigns, where static lists are managed using no-code tools like SFTP or Google Drive.
Analyzing historical trends is another area where batch processing works best. Examining years of transaction data to uncover market patterns requires comprehensive datasets processed during off-peak hours. Similarly, tasks like end-of-month commission calculations for agents or quarterly property valuation updates across thousands of listings are handled efficiently with scheduled batch cycles.
For CRM database maintenance, batch updates help cleanse and standardize records. Using tools like CASS Certification and Delivery Point Validation, addresses can be aligned with USPS standards. This periodic "hygiene" approach is far more economical than processing records individually in real time.
Use Case Table: Trigger-Based vs. Batch Updates
| Scenario | Best Method | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Instant Skip Tracing | Trigger-Based | Provides immediate contact details for fast outreach. |
| Fraud/Lien Detection | Trigger-Based | Delivers real-time alerts to avoid high-risk decisions. |
| Live Listing Updates | Trigger-Based | Keeps status changes visible, preventing outreach on unavailable listings. |
| Off-Market Deal Sourcing | Trigger-Based | Alerts investors instantly when acquisition criteria are met. |
| Monthly Market Reports | Batch Updates | Analyzes long-term trends without requiring instant updates. |
| Bulk Data Enrichment | Batch Updates | Processes large datasets efficiently for CRM enhancement. |
| Historical Trend Analysis | Batch Updates | Examines extensive data for strategic insights. |
| Direct Mail Campaigns | Batch Updates | Manages static lists effectively through no-code delivery methods. |
| CRM Database Cleansing | Batch Updates | Standardizes and updates thousands of records at once. |
Combining Both Approaches for Better Results
The smartest real estate data strategies don’t make you pick sides between trigger-based updates and batch processing – they combine both. By blending these approaches, platforms can respond to immediate, high-priority events with real-time triggers while keeping their databases up-to-date through scheduled batch updates. This hybrid system ensures that all data needs are met without overwhelming your resources or budget.
Here’s how it works in practice: trigger-based systems, like BatchData’s Smart Search API, send instant notifications via webhooks when specific events occur – think a property entering pre-foreclosure or hitting a certain equity level. At the same time, nightly batch updates refresh massive datasets with critical information, such as tax assessments, ownership changes, or property details and skip tracing. Triggers handle the urgent "act now" moments, while batch updates maintain a solid, up-to-date foundation of data. Together, these methods create a more efficient and streamlined workflow.
One major benefit of this approach is that it eliminates "polling", where systems repeatedly check for changes. Instead, webhooks push updates only when specific conditions are met, cutting down on infrastructure costs and reducing technical headaches. For teams without developers, BatchData simplifies things further by automating batch file deliveries to platforms like SFTP, Amazon S3, or Google Drive. Meanwhile, developers can integrate webhooks to ensure instant updates to CRMs or other tools.
The results speak for themselves: trigger-based marketing campaigns can boost customer engagement by 20–30%, thanks to delivering timely, relevant messages. When you pair this with batch-enriched databases that provide detailed property insights and historical trends, you get the best of both worlds. Investors can act quickly on new opportunities while making decisions backed by robust, comprehensive data. This balanced strategy keeps operations efficient, costs manageable, and ensures no valuable lead or insight slips through the cracks.
To make this work, define which events require immediate action – price drops, new listings, or status changes – and route these through webhooks. Use batch processing for larger, less time-sensitive tasks like market reports or CRM cleanups. With access to over 600 million records across property, address, and phone categories, refreshed daily, BatchData supports both strategies seamlessly. As your business scales, this flexible system grows right along with you.
Conclusion
Deciding between trigger-based updates and batch processing isn’t about picking a winner – it’s about matching the approach to your business needs. Trigger-based systems are perfect for delivering instant notifications when speed is critical, like pre-foreclosure alerts or timely new listings. On the other hand, batch updates shine when it comes to efficiently handling large volumes of historical data, such as creating monthly market reports or enriching CRM databases in bulk. The real question is whether the need for immediate action justifies investing in real-time infrastructure or if broader data coverage holds more value.
Many successful real estate platforms combine both approaches. They handle urgent, time-sensitive events using webhooks while ensuring database accuracy through scheduled updates. This hybrid strategy avoids the inefficiencies of constant polling, reduces infrastructure costs, and keeps your data fresh and actionable. As Chris Finck, Director of Product Management, explains:
"What used to take 30 minutes now takes 30 seconds".
This approach blends technical efficiency with the speed needed for actionable insights.
For teams adopting this hybrid model, BatchData provides tools to support both needs. Their real-time APIs deliver instant property intelligence for developers, while automated file deliveries to Amazon S3, Google Drive, or SFTP cater to teams without technical expertise. With a dataset refreshed daily, you can target high-equity absentee owners with precision or analyze broad market trends effectively.
The takeaway? Align your data update strategy with your team’s workflow. Use triggers for time-sensitive lead generation and batch processing for analytics and large-scale operations. When your data strategy reflects your operational priorities, whether through real-time updates or scheduled batches, your team can focus less on chasing data and more on closing deals.
FAQs
How do I decide which events should be trigger-based?
When you need actions to happen right away, trigger-based events are the way to go. Think about scenarios like new property listings, status changes, or lead alerts – these demand immediate responses to keep users engaged and enable quick decision-making.
On the other hand, for tasks that aren’t as time-sensitive, such as updating large amounts of property data or syncing information periodically, batch processing is a better fit. It works asynchronously, handling big datasets without putting too much strain on the system.
What happens if a webhook update is missed or arrives out of order?
Missed or out-of-order webhook updates can lead to data gaps or inconsistencies, which can disrupt the flow of information. These issues often stem from factors like network interruptions, server malfunctions, or rate-limiting constraints. To tackle this, many systems implement strategies such as retries, queuing, timestamps, or sequence numbers to maintain data accuracy and order.
Effective error handling and detailed logging play a critical role in identifying and resolving these problems quickly. By addressing such issues promptly, real estate platforms can ensure their data remains accurate and up-to-date, supporting seamless operations.
What’s the simplest way to combine triggers with nightly batch refreshes?
To make the most of triggers alongside nightly batch refreshes, you can set up table update triggers to keep an eye on changes in your source tables. These triggers can kick off batch processes whenever updates occur. At the same time, schedule nightly refreshes during low-traffic hours to ensure consistency and minimize disruptions. This mix of real-time updates and scheduled refresh cycles strikes a balance, keeping your data current while maintaining efficiency.



