APIs simplify bulk data syncing by automating large-scale data transfers between platforms like CRMs and external systems. They handle high volumes of data efficiently, processing thousands or millions of records asynchronously to prevent delays and system timeouts.
Key points:
- Bulk APIs are designed for high-volume operations, splitting data into manageable batches (e.g., up to 10,000 records) for faster processing.
- Industries like real estate and insurance use APIs to sync datasets such as MLS listings, property valuations, and contact records.
- Asynchronous processing ensures tasks run in the background, making it ideal for datasets exceeding 50,000 records.
- Bidirectional syncing prevents duplicate entries by using unique identifiers like external IDs.
- Real-time syncing updates records instantly for smaller tasks, while scheduled batch syncing handles large-scale imports during off-peak hours.
Everything You Need To Know About The Bulk API 2.0
How Bulk Data Syncing Works with APIs
Syncing data through APIs creates a direct pathway between your CRM and data sources. This process revolves around API endpoints, which are specific web addresses designed to accept data requests. For bulk operations, you set up a "job" that defines the task – whether it’s inserting, updating, or deleting data – and specifies the target dataset. To handle large datasets, the data is broken into batches of up to 10,000 records, enabling the server to process these batches simultaneously. This method is key to efficient asynchronous processing, especially when working with high volumes of data.
Asynchronous processing allows the server to manage requests in the background. Unlike standard REST or SOAP APIs, which operate synchronously and wait for an immediate response, bulk APIs handle data asynchronously. This approach eliminates the need for instant replies, making it ideal for datasets exceeding 50,000 records. In fact, Salesforce specifically recommends bulk operations for handling such large volumes.
To maintain consistency across platforms, bidirectional syncing comes into play. This process relies on upsert logic, which uses a unique external ID to update or insert records as needed. By preventing duplicate entries, this method ensures both systems stay aligned. A recent case study highlighted how automated syncing streamlined a large-scale data migration.
Core API Features for Bulk Data Syncing
Several features enhance the efficiency of bulk syncing, building on the foundation of asynchronous operations. These include batch endpoints, rate limit management, and state tracking:
- Batch endpoints: These handle multiple records in one API call, making them far more efficient than sending thousands of individual requests. For instance, Salesforce Bulk API 2.0 reduced the number of requests needed for a query from six to three. In contrast, standard REST API calls can only handle 2,000 records per response.
- Rate limit management: To avoid exceeding daily API call quotas set by most CRMs, bulk operations help you stay within limits. You can track your usage via the
/limitsendpoint or your CRM’s system overview page. - State tracking: This feature monitors the progress of your job through stages like
Open,UploadComplete,Processing, andJobComplete, giving you a clear view of when your data is ready.
These features are particularly useful for industries like real estate, where syncing property data or contact records is common. Platforms such as BatchData (https://batchdata.io) offer specialized API solutions designed to handle robust bulk data syncing and enrichment.
Real-Time vs. Scheduled Syncing
The timing of data syncing depends on your business needs. It can happen in real time or be scheduled for batch processing:
- Real-time syncing: This method uses REST APIs or Pub/Sub mechanisms to update records immediately as changes occur. It’s perfect for scenarios like updating a single property or modifying a contact record on the fly. However, because real-time APIs operate synchronously, they are better suited for handling smaller volumes of records rather than thousands at once.
- Scheduled batch syncing: Bulk APIs are ideal for large-scale operations, such as nightly imports of property records or contact databases. Data is submitted in formats like CSV, JSON, or XML, and the server processes it asynchronously. Results are accessible for up to seven days, compared to just two days for standard query cursors. This approach reduces API calls and prevents timeouts when managing datasets with hundreds of thousands of records.
Your choice between these methods should align with your use case. For instant updates in mobile apps or web interfaces, real-time syncing is the way to go. But for tasks like initial data loads, mass updates, or regular imports of MLS listings and property valuations, scheduled batch syncing is far more practical. Many organizations combine both methods – using real-time APIs for immediate updates and bulk APIs for routine, large-scale data transfers.
How to Set Up Bulk Data Syncing
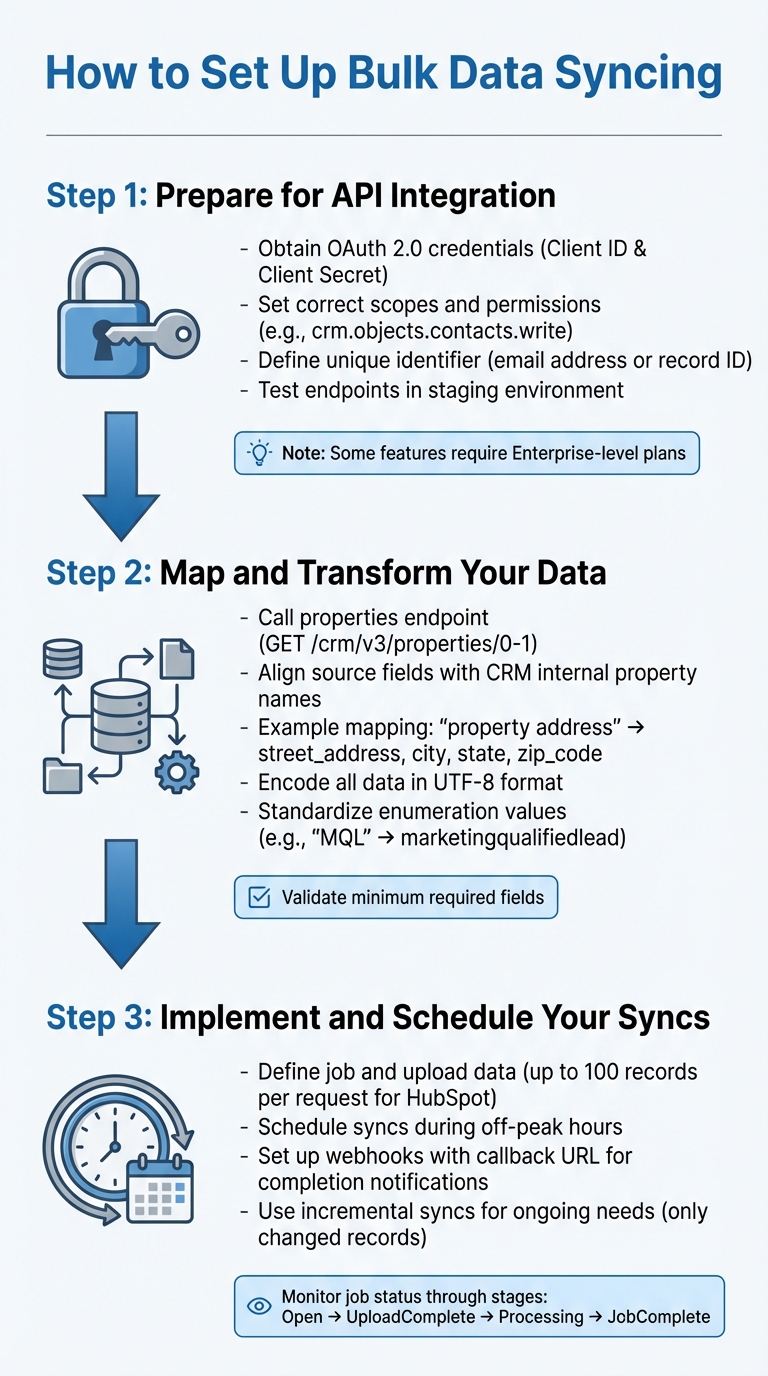
3-Step Process for Setting Up Bulk API Data Syncing
Bulk data syncing involves three main steps: obtaining API credentials, mapping fields, and scheduling syncs.
Step 1: Prepare for API Integration
Start by securing API credentials and permissions for bulk data syncing. Most modern CRMs, like HubSpot or Salesforce, rely on OAuth 2.0 authentication. This means you’ll need to create a Connected App or developer account to get a Client ID and Client Secret. These credentials allow you to generate an access token, which authorizes your API requests.
Be sure to set the correct scopes and permissions to define the level of access your API will have. For example, HubSpot requires specific scopes like crm.objects.contacts.write if you want to modify contact records. Keep in mind that some bulk features may only be available on higher-tier plans. For instance, HubSpot’s batch upsert functionality for certain objects is limited to Enterprise-level subscriptions.
To prevent duplicate records, define a unique identifier such as an email address or record ID. HubSpot highlights this point:
Email address is the primary unique identifier to avoid duplicate contacts in HubSpot.
Finally, test your API endpoints thoroughly in a staging environment before moving to production.
Once your credentials and identifiers are ready, you can move on to mapping your data.
Step 2: Map and Transform Your Data
Data mapping ensures that fields from your source system align with the CRM’s internal property names. To get started, call the CRM’s properties endpoint (e.g., GET /crm/v3/properties/0-1) to retrieve the internal names and data types for each field. This is important because CRMs often require system-specific names rather than user-friendly labels, especially for fields like picklists or enumerations.
For example, if you’re syncing property data from BatchData, a field like "property address" might need to be split into street_address, city, state, and zip_code in your CRM. Similarly, phone numbers from skip tracing should be validated and formatted to the CRM’s expected style – typically (XXX) XXX-XXXX for U.S. numbers.
Make sure all data is encoded in UTF-8 to avoid character corruption during the upload process. Standardize any values for enumerations to match the CRM’s accepted formats. For instance, convert "MQL" to marketingqualifiedlead if that’s the format required. Also, confirm that every record includes the minimum required fields before starting the sync.
Once your data is mapped and properly formatted, you’re ready to implement the syncing process.
Step 3: Implement and Schedule Your Syncs
To implement bulk syncing, you’ll need to define a job, upload your data, and monitor its status. For example, HubSpot uses a batch upsert endpoint where you can send a POST request with a JSON array containing up to 100 records per request. Salesforce Bulk API 2.0 follows a job-based workflow: create the job, upload the data as a CSV, and then close the job to start processing.
For large-scale operations, consider using a staging area to temporarily store data before the final sync.
Schedule syncs during off-peak hours to minimize the risk of delays caused by high server load. Instead of constantly polling the API for updates, set up a webhook with a callback URL so the CRM can notify your system once the sync is complete. For ongoing syncing needs, incremental syncs are a great option – they only update records that have changed since the last sync, reducing API calls and improving efficiency.
sbb-itb-8058745
Common Challenges and Solutions
Syncing bulk data through APIs often comes with its own set of hurdles. Once the initial setup is complete, real-world challenges tend to emerge. One common issue is schema mismatches. For instance, your source system might use a field name like customer_id, while the target CRM expects id. Or, one system may store a value as an integer while the other requires it as a string. These mismatches often occur when schema updates happen without informing the sync team. The solution? Use tools that automate schema mapping and maintain thorough documentation of any field structure changes.
Another frequent problem is duplicate records, which often arise during retries after timeouts or connection failures. Without a unique identifier, the system might create duplicate entries. To prevent this, include an identifierFieldName in your sync requests. This ensures that records – whether identified by an email address or a record ID – are updated correctly instead of being duplicated.
API limit violations can also disrupt sync processes. For example, Oracle Eloqua caps requests at 32 MB when posting data to its staging area, and many REST APIs limit responses to 2,000 records per call. Exceeding these limits can result in errors like "404 Not Found." To tackle this, break large datasets into smaller chunks, use GZIP compression to reduce payload sizes, and schedule syncs during off-peak hours to avoid server congestion.
Then there’s the issue of two-way sync conflicts, which occur when both systems update the same record simultaneously. This can lead to data overwrites or values flipping back and forth. Without clear rules, two-way syncs can cause chaos. To avoid this, establish conflict resolution rules upfront – such as using a "latest update wins" policy or designating one system as the primary source of truth. These steps help manage the complexities that arise after setup, ensuring smoother operations.
Fixing Data Conflicts and Sync Errors
When sync errors occur, the first step is to pinpoint their cause. Many bulk APIs provide detailed error logs that specify which records failed and why. For example, Salesforce Bulk API 2.0 offers "Failed Record Results" after a job completes, highlighting validation errors or field mismatches. Reviewing these logs immediately after each sync helps catch recurring issues.
Connection timeouts are another common obstacle, especially during large-volume syncs over slow or unstable networks. Using a callbackUrl can help here. This lets the system notify your server when the sync completes or fails, reducing unnecessary API traffic and ensuring you don’t miss critical updates.
To avoid syncing outdated data or performing unnecessary full-table refreshes, consider incremental syncing. By using last_updated timestamps or audit tables, you can sync only the records that have changed since your last update. This approach speeds up the process and minimizes conflicts.
"Change detection isn’t just a detail – it’s the core of smart synchronization".
For data format issues, pay close attention to line-ending requirements. Bulk API 2.0 jobs, for instance, may require specific formats (LF vs. CRLF) depending on the operating system used to generate your CSV files. Incorrect settings can lead to processing failures.
Finally, staging areas serve as a safety net. Upload data to a temporary staging area, validate the records, and then trigger the final sync. These areas typically retain data for 7 to 14 days before automatic deletion, giving you time to address any errors before they impact production.
| Common Sync Error | Primary Cause | Recommended Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Schema Mismatch | Field name or data type changes | Use automatic schema mapping and maintain clear documentation |
| Duplicate Records | Lack of unique identifiers | Include identifierFieldName to match records accurately |
| Sync Timeouts | Large payloads or slow servers | Break datasets into smaller segments and use GZIP compression |
| Data Overwrites | Concurrent updates in two-way sync | Set "latest wins" or "system priority" conflict resolution rules |
| 404/Request Errors | Exceeding payload size limits | Compress payloads and schedule syncs during off-peak hours |
Once these errors and conflicts are addressed, the next step is ensuring data security and compliance.
Security and Compliance Best Practices
Protecting sensitive data during bulk syncing requires a multi-layered security approach. Start by using strong authentication protocols like OAuth 2.0, which is widely supported by modern CRMs. For additional security, consider using JSON Web Tokens (JWT) or SAML 2.0, ensuring only authorized systems can access your data.
All API calls should be made over HTTPS connections with SSL/TLS encryption. While one-way SSL is common, two-way (mutual) SSL with CA-signed certificates offers stronger authentication by verifying both the client and server identities. This is especially important when dealing with sensitive information.
Granular access control is another critical safeguard. Use scopes to limit API permissions to only the actions required for your sync (e.g., crm.objects.contacts.write for updating contact records). Named credentials can also prevent the hardcoding of sensitive information, streamlining authenticated callouts.
To ensure data remains unaltered during transit, implement data integrity checks using digital signatures or one-way hashes with cryptographic functions. This adds an extra layer of protection against tampering.
For compliance with privacy regulations like GDPR, set up automatic data retention policies using parameters like autoDeleteDuration or dataRetentionDuration. This ensures sensitive data is purged from staging areas after the sync is complete, reducing the risk of breaches. Considering the 2.5 quintillion bytes of data created daily, secure synchronization is more important than ever.
Lastly, rate limiting and throttling can protect your systems from traffic surges during large data transfers. These measures prevent system overloads while ensuring legitimate sync operations proceed smoothly. For instance, if you’re syncing real estate data with BatchData, these safeguards allow you to transfer large volumes of property records without overwhelming your CRM’s infrastructure. Addressing these aspects ensures a secure and efficient data syncing process, ready to handle even the most demanding tasks.
Conclusion
APIs have revolutionized how businesses handle bulk data syncing, enabling the seamless processing of thousands – even millions – of records in the background without disrupting real-time operations. This automation is the backbone of the streamlined workflows discussed throughout this guide.
By relying on identifier fields and structured data formats, APIs ensure precision, reducing common issues like duplicate records or mismatched entries. Whether managing modest datasets or handling high-volume operations, APIs provide the tools needed to maintain accuracy and efficiency.
This capability is especially critical in industries like real estate. For instance, BatchData APIs excel in high-volume data management by instantly enriching property records with verified owner contact details, covering nearly 98% of the U.S. population.
"BatchData’s platform specializes in instantly enriching property records with verified owner details… making it a go-to solution for organizations focused on lead generation and outreach."
- Global Real Estate Watch
FAQs
How do asynchronous APIs prevent timeouts during bulk data syncing?
Asynchronous APIs manage bulk data syncing by breaking down large datasets into smaller, independent batches. These batches are then queued as background tasks and processed simultaneously, which helps maintain efficiency and makes scaling more manageable.
Rather than keeping the client waiting for the entire process to finish, the API quickly responds with a status token. This method avoids lengthy HTTP requests that could time out and ensures the system can handle extensive data transfers without interruptions.
What’s the difference between real-time syncing and scheduled batch syncing with APIs?
Real-time syncing delivers instant, incremental updates by transmitting small bits of data as changes happen. This approach works best for applications that demand the latest information, like live property status updates or enriching leads in real time.
On the flip side, scheduled batch syncing processes large chunks of data at predetermined intervals – whether that’s daily, weekly, or monthly. This method shines when dealing with tasks like transferring historical data, running overnight data loads, or managing large updates during less busy periods.
In essence, real-time syncing is all about quick, low-latency updates, while batch syncing focuses on handling high-volume transfers. Both options make the most of the BatchData API to cater to different requirements.
How can I prevent schema mismatches during bulk data syncing?
To prevent schema mismatches during bulk data syncing, it’s crucial to start with a well-defined and consistent data model. This model should serve as the single source of truth for your operations. Leverage the API’s field-mapping tools to align incoming data with your target schema before the syncing process even begins.
Another essential step is validating data payloads on both ends – sending and receiving. Incorporate schema validation techniques, like JSON schema checks, to identify and address missing or incorrect fields early in the workflow. Doing so ensures data accuracy and reduces the risk of errors.
Lastly, think of your integration definitions as unchangeable contracts. Avoid altering active definitions during a sync. Instead, create new definitions or temporary ones for specific, one-time tasks. These strategies help maintain consistency and ensure your data syncs smoothly without introducing unnecessary errors.