Undeliverable mail caused by inaccurate address data costs U.S. businesses over $20 billion annually. A mailing address validator is an automated system designed to parse, standardize, and confirm the physical deliverability of mailing addresses against official postal databases. This tool transforms raw, error-prone data into a reliable business asset, preventing wasted marketing spend, returned shipments, and compliance failures before they happen.
| Core Takeaway | Description |
|---|---|
| Problem | Bad address data leads to wasted money, operational drag, and poor customer experiences. |
| Solution | A validator cleans, standardizes, and confirms addresses against official sources like the USPS. |
| Methods | Real-time APIs prevent bad data at entry; batch processing cleans existing databases. |
| Impact | Increases marketing ROI, improves efficiency, ensures legal compliance, and powers accurate analytics. |
This guide explains precisely how these tools operate, how to integrate them, and why they are a non-negotiable asset for any data-driven organization.
What Are the Direct Costs of Inaccurate Addresses?
Bad address data is a direct financial leak that erodes profits and operational efficiency, representing far more than just the cost of a lost stamp. Every piece of returned mail signifies wasted printing, postage, labor, and a missed opportunity to connect with a customer. For data-intensive industries like real estate, a single incorrect address can derail a critical legal notice, sink a property acquisition campaign, or skew the underwriting analysis a major deal hinges on.
The core function of a mailing address validator is to mitigate financial and operational risk. It shifts an organization from a reactive mode—dealing with returned mail and frustrated customers—to a proactive one where data integrity is foundational.
The True Cost of Bad Data
The cost of bad address data cascades far beyond postage, creating ripple effects across marketing, operations, and analytics that damage brand reputation. Each error introduces friction, from delayed critical shipments to direct mail campaigns that never reach their intended audience. A marketing team might see response rates plummet and assume the offer was weak when the real culprit was a significant portion of mailers ending up in a dead-letter office. Clean address data is also essential for complex logistical puzzles like route optimization for last mile delivery.
Core Problems Solved by Address Validation
Implementing a robust mailing address validator is a direct investment in efficiency, customer satisfaction, and reliable business intelligence. By solving the foundational problem of data accuracy, you unlock superior performance across your entire organization.
| Problem Area | Impact of Inaccurate Data | How a Validator Provides The Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Marketing ROI | Wasted spend on undeliverable mail, low campaign response rates, and skewed performance metrics. | Maximizes deliverability, ensuring marketing materials reach the intended audience so ROI can be measured accurately. |
| Operational Efficiency | Increased costs from returned shipments, frustrating address correction fees from carriers, and hours wasted on manual data cleanup. | Standardizes addresses to precise USPS specifications, slashing carrier fees and nearly eliminating returned mail from formatting errors. |
| Customer Experience | Delayed deliveries, failed communications, and deep customer frustration that leads to churn and negative reviews. | Ensures products and communications arrive reliably and on time, which is fundamental for building customer trust and satisfaction. |
| Compliance & Legal | Serious risk of non-compliance with regulations (e.g., KYC, legal notices) by sending official documents to the wrong addresses. | Verifies addresses physically exist and are mailable, providing a critical layer of due diligence for mandatory communications. |
| Data Analytics | Flawed customer segmentation, inaccurate geographic analysis, and business intelligence built on a shaky foundation. | Provides a clean, standardized dataset that powers accurate location-based insights, market analysis, and confident strategic planning. |
How Does a Mailing Address Validator Work?
A high-quality mailing address validator systematically breaks down, cleans, and cross-references address entries against official postal sources to confirm an address is real and mailable. The process takes raw, inconsistent inputs like "123 main street, apt 4, newyork" and transforms them into perfectly formatted, USPS-compliant addresses that automated sorting machines can process without error. This transformation turns chaotic raw data into a structured, clean asset.
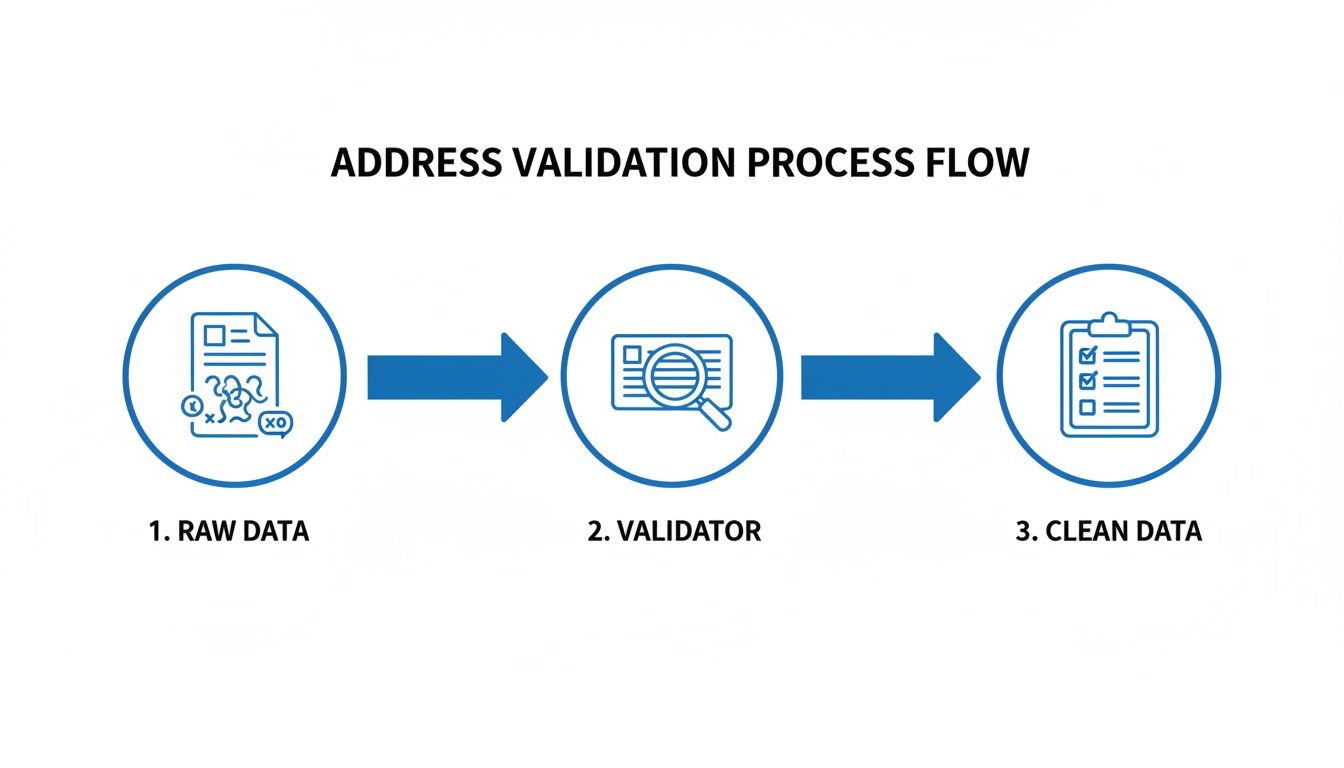
Parsing and Standardization
The first step is parsing, where the system dissects a single line of text into its fundamental components. It intelligently identifies and separates the street number, street name, city, state, and ZIP code into distinct fields. Once parsed, the address undergoes standardization, a critical step where informal terms are translated into the official format recognized by postal services.
- Street Suffixes:
StreetbecomesST,AvenuebecomesAVE,RoadbecomesRD. - Directionals:
Northis converted toN,SouthwestbecomesSW. - Secondary Units:
Apartmentis changed toAPT,SuitebecomesSTE.
This isn't merely cosmetic; standardization enables high-speed postal sorting equipment to process mail accurately, reducing manual intervention and delivery delays.
Core Validation
With the address parsed and standardized, the validator performs its most critical function: validation. The system cross-references the cleaned-up address against an authoritative database—in the United States, this is the USPS Coding Accuracy Support System (CASS). This check answers one vital question: Does this physical address actually exist and can it receive mail?
A CASS-certified system confirms that the combination of street name, number range, and ZIP code is a legitimate, mailable location. For example, an address like 789 Oak Ave might be perfectly formatted, but if the highest number on Oak Avenue is 600, the CASS check will flag it as invalid.
Industry data suggests up to 23% of all customer and prospect data contains critical errors that make it undeliverable. Validation moves you beyond guesswork to data-driven certainty.
Geocoding and Deliverability
Modern validators add extra layers of intelligence like geocoding. This process assigns precise latitude and longitude coordinates to the validated address, turning a mailing location into a pinpoint on a map. Another advanced feature is the deliverability check, which uses additional data sources to determine if a valid address is currently able to receive mail.
It identifies conditions that will cause returns:
- Vacant Properties: Flags addresses known to be unoccupied.
- No Mail Receptacle: Identifies locations that lack a mailbox.
- Commercial Mail Receiving Agency (CMRA): Pinpoints addresses at private companies like The UPS Store.
These checks provide deeper insight, helping businesses avoid sending mail to locations where it has zero chance of being received.
Which Integration Method Is Right for You: Real-Time API vs. Batch Processing?
The decision between a real-time API and batch processing depends entirely on your business objective. A real-time API acts as an instant check to prevent bad data from entering your systems, while batch processing is a heavy-duty tool for cleaning large, existing datasets. Making the right choice directly impacts data quality, user experience, and operational efficiency.

Real-Time API
A real-time API integration is like a bouncer for your database, checking each address the moment a user types it into a web form, CRM, or e-commerce checkout. Since over 80% of data quality issues originate at the point of capture, an API stops the problem before it starts by providing immediate feedback and correcting typos as they happen. It is the best method for any system where users are actively entering address data.
Use cases include:
- E-commerce Checkouts: Suggests corrections as a customer types, reducing cart abandonment and failed deliveries.
- CRM Data Entry: Ensures sales and support teams add deliverable addresses from the start.
- Lead Capture Forms: Immediately improves the quality of marketing leads from your website.
A real-time API is fundamentally a user experience tool. By confirming an address is deliverable before a user submits a form, you build trust and reduce operational friction. For a better feel for the technical side, take a look at our guide on how to set up a real estate API integration or see how similar automated checks apply in a WooCommerce Shipping Restrictions API Integration.
Batch Processing
Batch processing is the specialized cleanup crew for messes that already exist. This method is designed to process massive datasets all at once. You upload a file with thousands or millions of addresses, and the system returns a clean, standardized, and validated list. It is the most efficient method for working with "data at rest."
Use cases include:
- Direct Mail Campaign Preparation: Run your entire list through a batch validator before printing to maximize deliverability and stop wasting postage.
- Database Cleansing: Perform a quarterly audit of your contact database to correct, standardize, and flag invalid records.
- Data Migration: Use batch processing to ensure only clean, validated addresses are moved to a new system.
Comparison Table: API vs. Batch
| Attribute | Real-Time API | Batch Processing |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use Case | Point-of-entry validation (web forms, CRM, checkout). | Cleansing and validating large, existing datasets. |
| Data Flow | Synchronous; one address at a time, instant response. | Asynchronous; processes a large file, returns it later. |
| Speed | Milliseconds per address. | Minutes or hours for the entire file, depending on size. |
| User Experience | High; provides immediate feedback and suggestions. | Low; an internal process with no direct user interaction. |
| Best For | Proactive data quality, fraud prevention, UX enhancement. | Data hygiene projects, list preparation, database audits. |
| Technical Skill | Requires developer resources to integrate the API. | Minimal technical skill needed; often a simple file upload. |
Many organizations use a hybrid approach: a real-time API to guard all entry points for new data, and batch processing for periodic cleanups and special projects.
How Do You Measure Validator Performance and Accuracy?
To determine a validator's effectiveness, you must measure its performance with specific metrics, or Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). These numbers transform the abstract concept of "data quality" into a tangible business asset you can track, proving ROI and justifying the investment. Without clear benchmarks, you cannot know if your tool is saving money or how clean your data truly is.
Core Performance Metrics
Tracking KPIs provides a clear snapshot of how effectively the tool is cleaning and confirming your data.
- Accuracy Rate: The percentage of addresses the validator correctly identifies as valid or invalid. An ideal rate is 98% or higher.
- Match Rate: The percentage of addresses the system successfully matches in an authoritative database like USPS CASS. A low rate can signal messy initial data.
- False Positives/Negatives: A false positive is when the validator wrongly marks a bad address as good, leading to wasted postage. A false negative is when a good address is flagged as undeliverable, leading to missed opportunities.
These metrics should be monitored continuously. For guidance on setting up these benchmarks, see our guide on using a real estate data accuracy checker.
Match Confidence Score
For ambiguous addresses like "123 Main St" without a city, modern validators provide a match confidence score. This is a rating, typically from 0 to 100, indicating the system's certainty about the match it found. This score enables automated, risk-based decisions.
You can set business rules to automatically accept any address with a confidence score above 95, flag anything between 70-94 for manual review, and reject anything below 70. This creates an efficient workflow for handling ambiguous data without requiring human review of every record.
Calculating ROI
The ultimate goal is to connect these performance metrics to real business outcomes. Without validation, undeliverable mail can bloat campaign costs by 10-20%. By tracking the reduction in returned mail and its associated costs—printing, postage, handling—you can calculate the direct ROI of your validation tool. Globally, services tackle this challenge across 250+ countries; discover more insights about international address verification on loqate.com.
Why Is Address Validation Critical for Real Estate and Proptech?
In real estate, a physical address is the fundamental key that unlocks nearly every transaction, making a mailing address validator a core operational tool. The industry runs on the certainty that a piece of mail, whether a legal notice or a marketing offer, will reach the right property or owner. A pre-foreclosure notice sent to an invalid address can nullify the legal process, costing lenders thousands in delays and legal fees.
Driving Direct Mail and Skip Tracing
For real estate investors, direct mail success hinges entirely on deliverability. An address validator ensures every mailer sent to motivated sellers has the highest possible chance of arriving, maximizing reach and minimizing wasted spend. This technology is equally critical for skip tracing.
An address validator is the first step in this process. By confirming the property address is valid, it creates a reliable starting point to then append verified owner mailing addresses, phone numbers, and email contacts, turning a property record into an actionable lead.
North America holds a 37% share of the global address verification software market. Verified addresses ensure compliant mailings for pre-foreclosure notices, investor outreach, and insurance underwriting. In proptech, BatchData's verified owner contacts exemplify this, powering skip tracing across 155M+ records. You can read the full research about address verification software on fortunebusinessinsights.com.
Fortifying Underwriting and Risk Assessment
In mortgage lending and property insurance, a verified property address is the foundational data point for all underwriting models. Lenders and insurers use this validated location to pull critical data.
A validator's role:
- Accurate Valuations: Ensures Automated Valuation Models (AVMs) pull comparable sales data from the correct geographic area.
- Portfolio Analysis: Allows for precise geographic risk concentration analysis, helping institutions understand exposure to localized market shifts.
- Fraud Prevention: Helps flag fraudulent submissions tied to non-existent properties.
Ensuring Compliance
Certain real estate communications are legally mandated, like pre-foreclosure notices. Failure to deliver these notices due to an invalid address has serious legal and financial repercussions. An address validator provides essential due diligence by validating addresses before sending legally required mail, creating a defensible record of compliance. This simple step protects firms from legal challenges. For a deeper dive, learn more about real-time data accuracy in our article on property verification.
How Does Clean Address Data Become a Strategic Asset?
Clean, accurate address data is a strategic asset that creates powerful ripple effects across an entire business. The global address verification software market was valued at USD 935.16 million in 2021 and is projected to reach USD 2,758.15 million by 2030, a 12.63% CAGR driven by the mission-critical need for accurate addresses in e-commerce and digital services. This is no longer just a tool—it's foundational infrastructure. For a deeper analysis, you can discover more insights about the address verification market on geoiq.ai.
Bolster Compliance and Risk Management
In an era of tightening data privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA, address data quality is directly linked to compliance health. An incorrect address isn't just a bounced mailer; it's a potential compliance breach. Using a mailing address validator demonstrates due diligence and helps avoid sending sensitive information to the wrong person—a scenario that can lead to massive fines and reputational damage.
Accurate address data is a fundamental component of a modern risk management framework. It ensures you're communicating with the right individuals and respecting their data privacy rights.
Unlock Sharper Business Intelligence
Beyond mitigating risk, clean address data unlocks a richer understanding of customers and markets. When every address is validated, standardized, and geocoded, you can perform more sophisticated analysis.
- Precise Segmentation: Group customers into real geographic clusters to find high-value regions.
- Relevant Personalization: Use reliable location data to personalize offers, like notifying customers of a new local store.
- Optimized Operations: Improve sales territories, delivery routes, and resource allocation based on a clear map of your customer footprint.
A mailing address validator transforms messy location data into a reliable asset that builds stronger customer relationships and powers smarter, more profitable decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions About Address Validation
What is the difference between address validation and address verification?
The key difference is deliverability versus identity. Address validation confirms a mailing address physically exists and is formatted correctly for postal delivery (the 'where'). Address verification goes further to confirm a specific person or business is associated with that validated address (the 'who'). Validation is for mass mailings; verification is for high-risk transactions or identity confirmation.
How much does a mailing address validator service cost?
Most services operate on a pay-as-you-go model, charging fractions of a cent per lookup (API) or per record (batch). Enterprise plans offer bulk discounts or monthly subscriptions for high-volume users. Costs increase for advanced features like:
- Geocoding: Adding latitude and longitude coordinates.
- International Validation: Checking addresses outside the United States.
- Data Enrichment: Appending details like property owner information.
Can a validator handle international addresses?
Yes, but this capability separates basic tools from enterprise-grade services. While many validators are built for a single postal system like the USPS, advanced platforms support hundreds of countries and their unique address formats.
If your business operates across borders, confirming a provider's specific country coverage is non-negotiable. A validator without robust international support will create significant data gaps and operational headaches. Always verify a service’s global reach before committing.
Ready to transform your messy address data into a strategic asset? BatchData provides enterprise-grade property data, including a powerful mailing address validator and enrichment APIs, to ensure every record is accurate and deliverable. Explore our data and APIs today.